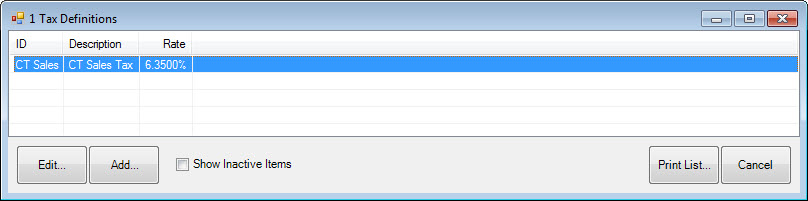
To set up and edit tax definitions:
1. Select Sales Tax from the Administrative menu.
2. Select Tax Definitions. The Tax Definitions window will appear.

3. To add a new tax, select Add. The New Sales Tax Definition window will appear with the General tab presented. To edit a tax definition, select Edit. The same window will appear, but will already be populated with data to edit.
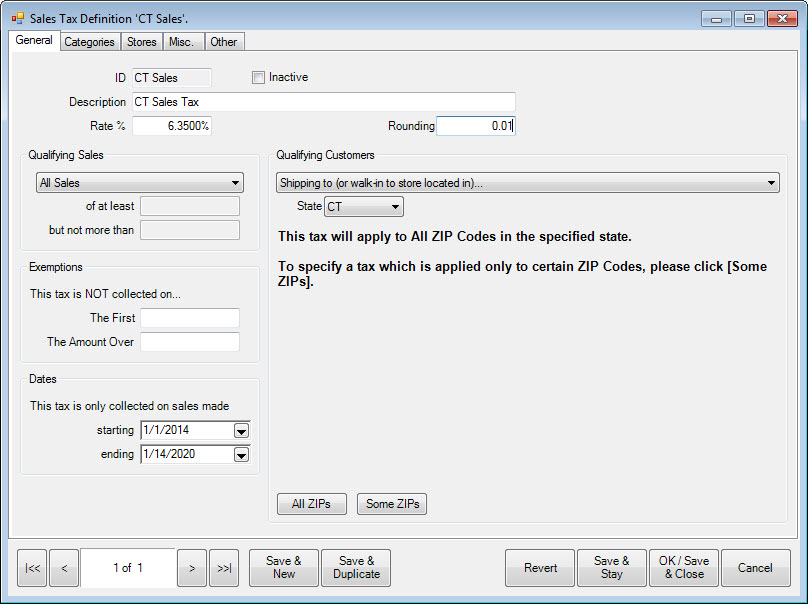
Fields and options in the General tab include:
|
ID |
The identification for the tax. This can be a number or short descriptor. | |
|
Inactive |
Indicates whether the tax is currently applicable. | |
|
Description |
A detailed description of the tax. | |
|
Rate % |
The percentage of sales to be collected. | |
|
Rounding |
To what decimal tax calculations should be rounded. | |
|
Qualifying Sales |
Allows you to define taxes based on prices or sales amounts. There are three categories, all of which offers different options for values: •All: All sales will be taxed at the rate specified. •Item: Specify a price range to be taxed on an item-by-item basis. For example, items of $0–$5,000 might not have this tax. Items of $5,000 and over might have it. If you want items over a certain amount, enter a value for of at least but leave but not more than blank. This is an example of how one jurisdiction might require more than one tax definition. •Sales Totaling: This is used just like Item, but only if the total sale drives the tax rate. | |
|
Qualifying Customers |
Allows you to specify certain categories of customers for whom the tax should be collected. The most common example would be the collection of tax for customers shipping within the state, but excluding tax on shipments to out of state destinations. This is set by using the Shipping to (or walk into store located) option. It can also be refined by ZIP Code for shipping. If you have selected Shipping to, the All ZIPs and Some ZIPs options will appear. | |
|
Exemptions |
Allows you to specify sales amounts for which the tax should not be collected. This is only item-by-item regardless of qualifying sales. This might be used in conjunction with Qualifying Sales and a number of tax definitions to layer progressive taxes. The exemption will apply as specified: | |
|
|
The First |
Tax will not be collected on the portion of the sale below this amount. |
|
|
The Amount Over |
Tax will not be collected on the portion of the sale above this amount. |
|
Dates |
Allows you to specify that the tax must only be collected during certain time frames. Be sure that if you have an expiring tax definition, that a new one will begin afterword. | |
|
|
Starting |
Date to start collecting the tax. |
|
|
Ending |
Last date to collect the tax. |
4. Complete the General tab fields as applicable.
5. Select the Categories tab.
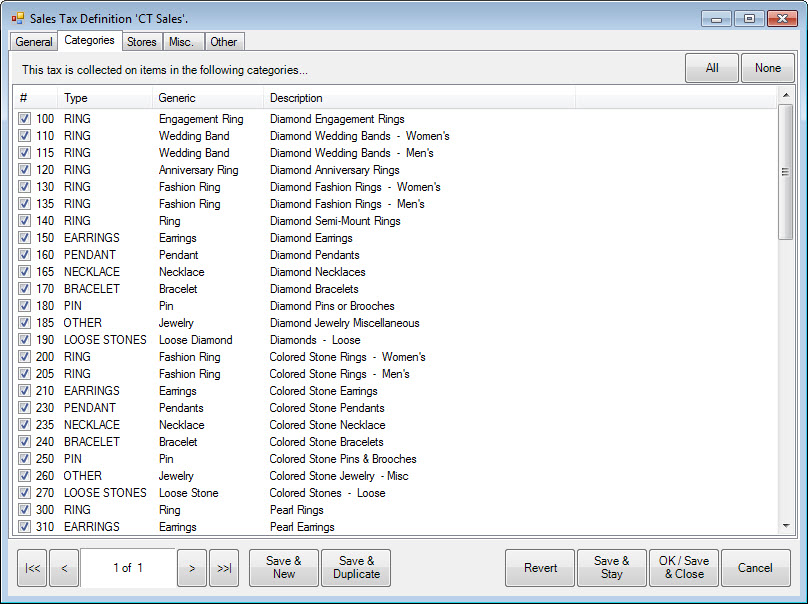
The Categories tab allows you to select categories of items for which the tax should be collected.
6. Select the desired categories.
7. Select the Stores tab.
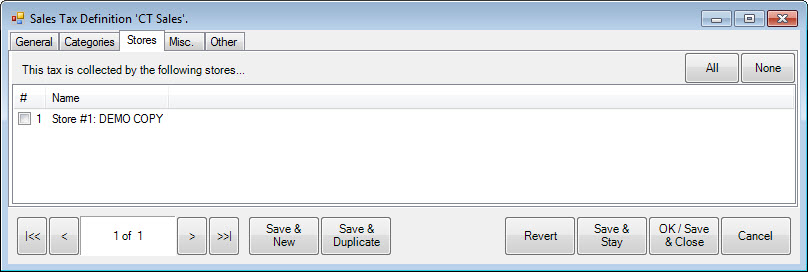
8. Indicate which stores will be required to collect the tax.
9. Select the Misc tab.
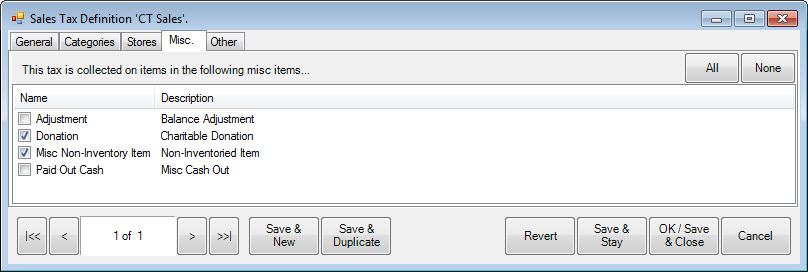
10. Indicate those miscellaneous items for which the tax must be collected.
11. Select the Other tab.
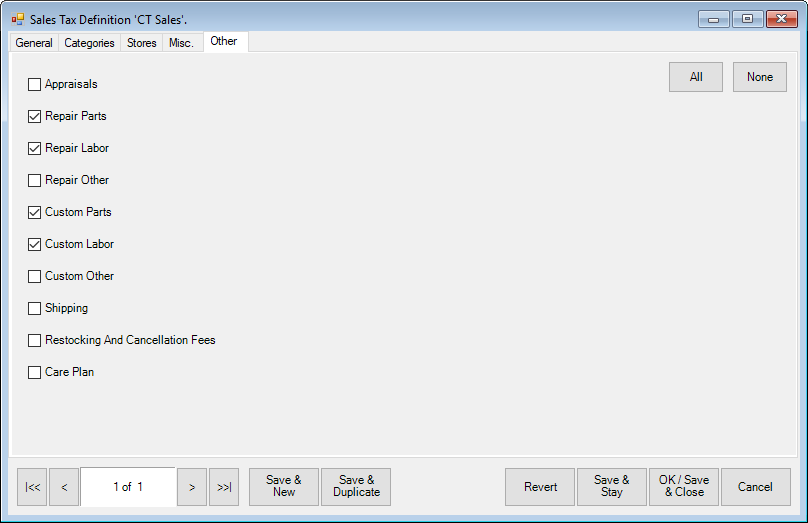
12. Indicate those services and repair items for which the tax should be collected.
13. Select the appropriate save option from the Record Navigation Bar.
Example:
Suppose you have a jurisdiction with a standard 6% sales tax on all items and a luxury tax of 8% that applies to any item costing more than $5,000 and is applied to only the amount over $5,000:
1. Create a tax definition for items at 6% with no exemptions.
2. Create a second tax definition for items over $5,000 at 2%.